Are all cryptocurrency exchanges built in the same way? Though centralized exchanges have existed for far longer, this market’s rise has spawned a whole new industry of decentralized applications that are the opposite of their counterparts.
The fundamental distinction over a CEX (centralized exchange) and DEX (decentralized exchange) is similar to the differences between fiat and cryptocurrencies, where the former is authority-controlled while the latter is user-powered. When you’re buying a digital coin, you may see discrepancies among centralized and decentralized exchanges.
While no one type is necessarily superior to the other (what matters more is the recognition and trustworthiness of an exchange), it is still beneficial to know the variances.
Firstly, let’s define a cryptocurrency exchange
Before understanding the contrasts between a CEX and DEX, it’s good to explore the definition of an exchange. A cryptocurrency exchange allows clients to trade a wide array of digital currencies against each other and other fiat currencies.
Users deposit their money via card payments, wire transfers, and other cryptocurrencies for the ability to buy and sell on the exchange’s platform. CEXs were naturally the first type of exchanges in the early 2010s, but through the years, a whole new industry of decentralized entities began emerging.
CEX
A centralized exchange is the archetypal type of regulated or licensed (though not every CEX is) financial business where a third party facilitates transactions and acts as a link between clients and the market itself. For their efforts, they will charge fees every time one buys or sells coins and makes withdrawals.
We should appreciate centralized exchanges that do far more in the background, making for a more pleasant customer experience. The critical element for CEX is control, which solely lies on their side. They will require your personal information as part of KYC (Know Your Customer) protocols.
Perhaps the biggest concern is the private keys and security of one’s funds lie in the hands of a CEX, a stark contrast to a DEX. It is not necessarily that these exchanges usually steal client funds (although ‘exit scams’ are likely with this model), but rather the exposure to hacking.
There have been numerous stories in the last decade of hacking incidents where hackers gained access to an exchange’s public key encryption and stole millions. Nonetheless, one outstanding attribute of CEX is the enormous access to independent market makers providing liquidity through an internal order book.
DEX
By design, decentralized exchanges run mostly autonomously and are the direct opposite of a CEX. Through the sentiments of many analysts, they represent how cryptocurrencies should operate; a DEX merely cuts out the middleman.
Users within the platform are essentially the liquidity providers and have more freedom, especially that an intermediary or custodian does not control the funds. Decentralized exchanges use a P2P model on a blockchain with distributed nodes or computers entrusted to meeting the consensus according to the exchange’s rules.
Unlike the order book used by market makers in CEXs, most DEXs rely on what is known as the AMM (automated market-making) model. The AMM involves pooling liquidity from users on DEX platforms and deriving the market through a deterministic algorithm.
While decentralization is an overarching theme here, most DEXs have little to no regulation, which may be a concern for some.
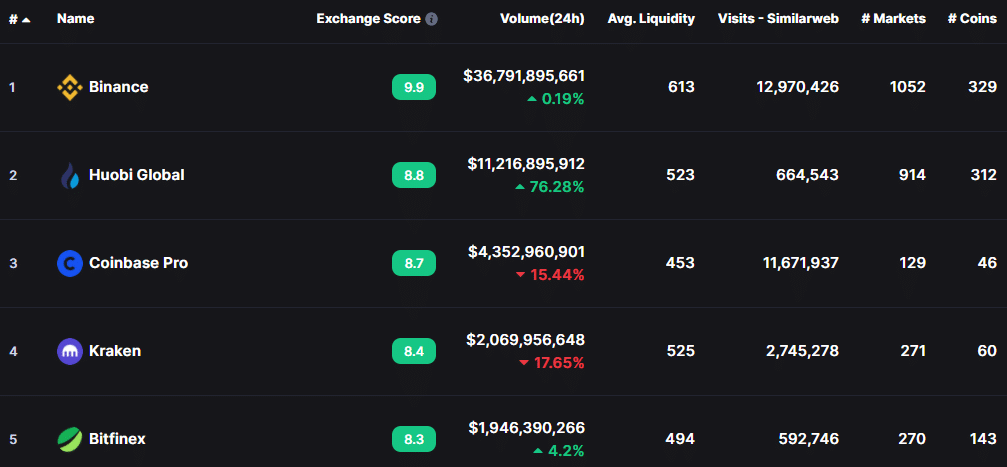
Top 5 centralized exchanges
Here is a list of the top 5 CEX by trading volume (as of 23 February 2020). The image below is from CoinMarketCap.
- Binance
- Huobi
- CoinBase
- Kraken
- Bitfinex
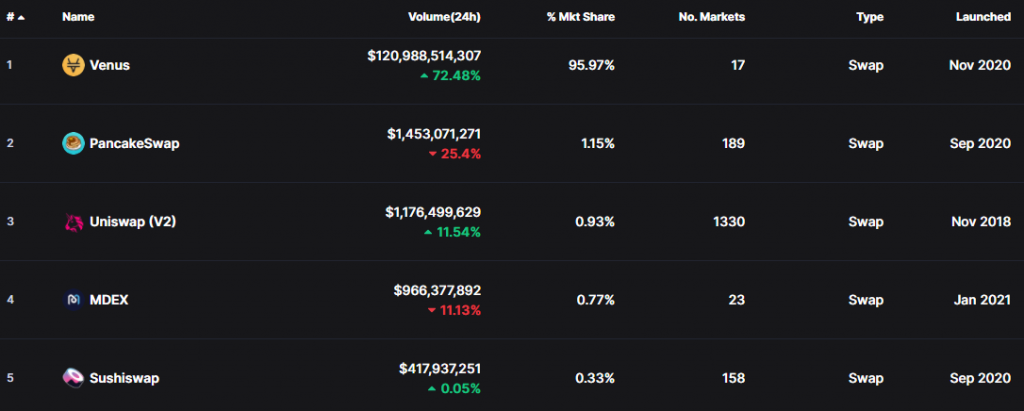
Top 5 decentralized exchanges
Here is a list of the top 5 DEX by trading volume (as of 23 February 2020). The image below is from CoinMarketCap.
- Venus
- PancakeSwap
- Uniswap
- MDEX
- Sushiswap
Pros and cons of CEX
Below are some of the main pros and cons of CEX.
Pros
- Superior liquidity. A centralized exchange has access to multiple liquidity providers worth millions of dollars. Therefore, buying and selling a cryptocurrency happens significantly quicker. There will always be a buyer or seller for any transaction regardless of the order size, dramatically reducing the chances of slippage.
- Regulation. As a regulated entity, most CEXs follow KYC procedures and are trusted to act ethically to their clients, especially in crisis events.
Cons
- Higher risk of hacking. We typically refer to CEX as custodial as they have complete control of client funds where they issue IOUs (I owe you) to them. They secure the funds mainly through public-key encryption, and while it is reliable and robust, it is highly susceptible to hacking risks.
- Fees charged on a regular basis. Overall, costs in cryptocurrency trades are still usually lower than in the traditional financial system. However, because of the infrastructure required for a CEX, they will typically charge for all transactions.
Pros and cons of DEX
Below are some of the main pros and cons of DEX.
Pros
- Lower risk of hacking. DEXs are non-custodial since they have no custody or control of their users’ funds. Therefore, clients are responsible for this security by keeping the private keys of the hot or cold wallets to themselves, making them less susceptible to the hacking of the entire exchange.
- More sensitive to personal data and wallet funds. Privacy is a key advantage of DEX as no entity has access to the keys of anyone’s funds. Anonymity in personal data is generally encouraged as many DEXs do not necessarily follow KYC.
- Lower or no fees. The design of many DEXs is actually to incentivize users rather than being a profit-driven organization.
Cons
- Lack of regulation. While there is no third-party body in DEX, having little or no regulation may be of concern to some.
- Lower liquidity. As DEXs don’t rely on an extensive network of large market makers, leaning towards their internal liquidity pools, executing trade orders cannot always happen in seconds as it does on CEX due to low trading volume. These events increase the chances of slippage and a special type of attack known as ‘front running.’
Conclusion
The table below outlines some general differences between CEX and DEX as a summary, including other points that weren’t significantly explored.
| Centralized cryptocurrency exchange | Decentralized cryptocurrency exchange | |
| Security | More susceptible to hacking risks | Less susceptible to hacking risks |
| Control | Users have little control | Users have more control |
| Liquidity | Higher; orders occur in seconds | Lower; orders may take a little longer to occur |
| Order book | Traditional | Automated |
| Fees | Yes | Charges little or none |
| Regulation | Usually regulated | Typically not regulated |
| Popularity | More popular | Less popular |
Though decentralization with cryptocurrencies is its ‘bargaining chip,’ there are some massive advantages about a CEX over DEX.
We cannot, however, ignore DEXs have been a massive trend, especially in the DeFi (decentralized finance) space that has disrupted many of the traditional finance systems we know. This article should serve as an educational guide about the differences between these exchanges and what one should expect from each.







