
Is Chainlink the unique cryptocurrency in the market? As its name suggests, Chainlink deals with ‘linking’ external data to blockchains through a technology known as oracles. While there are several digital currencies involved with smart contracts, Chainlink bridges the gap of feeding accurate, outside data back to such contracts.
Overview
Are you keen on knowing about a digital coin that’s pioneered an innovative technology? Enter Chainlink, one of the unique cryptocurrencies in the market, through their application of connecting real-world data to smart contracts on blockchains.
These terms may seem daunting to the laymen, though this article will decipher such ideas in the simplest way possible.
After hovering around the mark of 40 for much of 2019, Chainlink is now the seventh most traded digital asset, according to CoinMarketCap. It has a per-token value of about $23 and approximately $9.5 billion market capitalization (all stats correct as of 31 January).
Beginnings
The aptly named blockchain oracle developer, SmartContract (started in September 2014), co-founded by Steve Ellis and Sergey Nazarov, was the brains behind the coin.
After publishing the whitepaper for the platform, Chainlink had its ICO (initial coin offering) in September 2017, issuing 35% of the proposed 1 billion LINK coins and raising an impressive $32 million.
The remainder of the tokens were split as follows; 30% went to SmartContract to fuel the continual development of the network, and the remaining 35% is for node operators. Chainlink was created and still exists as the Ethereum-based ERC20 token.
At the time of writing, roughly 40% of LINK is presently circulating (about 404 million).
What is Chainlink?
How Chainlink operates is quite unique because of serving a high niche purpose, unlike other digital currencies. At its core, Chainlink incentivizes a global decentralized computer network (known as oracles or middleware) with its native cryptocurrency known as LINK to provide off-chain, real-world data to smart contracts.
Chainlink’s current slogan is “Connect your smart contract to the outside world.” To appreciate this tagline, we need to comprehend smart contracts. Ethereum was one of the first to bring life to the concept in 2015.
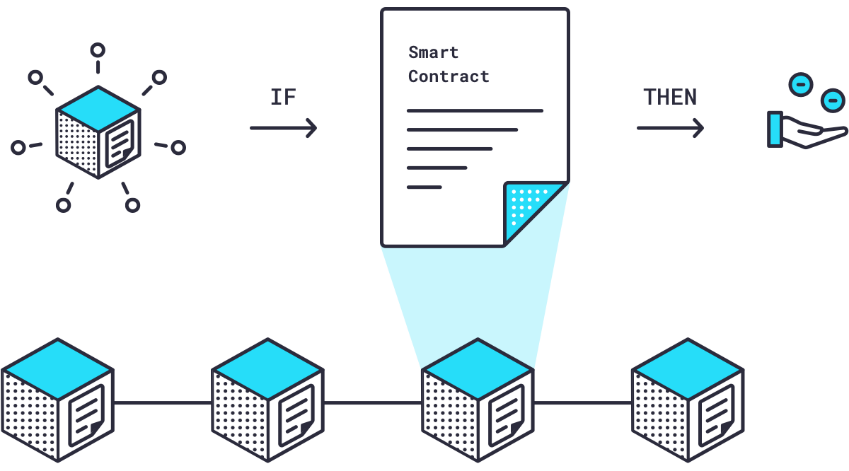
A smart contract is an autonomous, self-executing contract on a blockchain. However, a fundamental problem is the external data source that feeds a smart contract to execute its terms authentically.
These contracts need tamper-proof, reliable outside data, specifically APIs (application programming interfaces) in an on-chain format. To solve this challenge, Chainlink employs ‘oracles,’ which bridge the gap between smart contracts and external data feeds.
We can also liken oracles as ‘interpreters’ translating the languages between blockchain and external data.
How does Chainlink work?
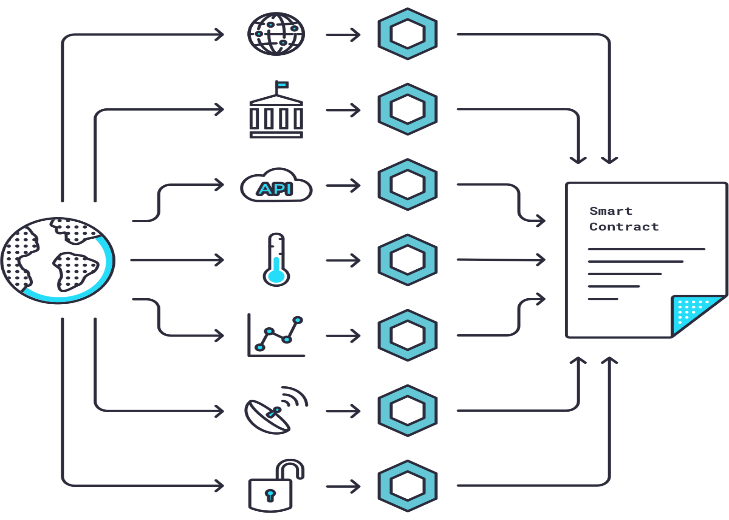
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network for smart contracts. These contracts frequently need external data feeds, and when they request for such, node or nodes will make API and other off-chain calls, evaluate the data, and return it back.
For this work, node operators are incentivized with LINK tokens if they’ve provided truthful information. The platform runs an intricate reputation system, assessing whether the data given is genuine.
Anyone can become a node operator or oracle if they meet the necessary computer requirements on the blockchain and have the expected technical knowledge. From a user perspective, LINK is available on plentiful cryptocurrency exchanges for trading and wallet storage purposes.
Is Chainlink a mineable coin?
Interestingly, Chainlink is neither a mineable nor a staked coin like several traditional cryptocurrencies. However, there is an element of staking involved depending on whether one becomes a node operator or an ordinary token holder.
Contract creators currently require node operators to stake a minimum of LINK tokens depending on the given task. Node operators partake in a bidding process for these jobs.
Although staking on the existing Chainlink network is not currently possible, external services running operator pools offer token holders the chance to receive income from the stakings of node operators. No accessible information seems to exist on what node operators earn from working on Chainlink.
What makes Chainlink valuable?
Chainlink is easily one of the genuinely distinctive cryptocurrency projects in history as it solves a niche and specific problem with blockchain connectivity. Everyone from big tech to blockchain corporations has taken an interest in or adoption of Chainlink’s technology.
Though what exactly is the challenge Chainlink is solving? We’ve already stated blockchains, and smart contracts cannot retrieve off-chain or external data, which is necessary to make them valid. Let’s illustrate with an example.
Let’s assume one needed a smart contract for a weather insurance premium. In order to define the terms and calculate an accurate rate, an oracle is necessary to fetch real-time weather data back into the blockchain.
Aside from insurance, Chainlink’s technology is applicable in a wide range of fields such as finance, gaming, supply chain, authorization, utilities, enterprise systems, blockchain interoperability, and many more.
Future of Chainlink
For anyone interested in the potential of Chainlink, we should appreciate that a field where cryptocurrencies may become more relevant is with dApps (decentralized applications), especially DeFi (decentralized finance).
The use of smart contracts was mainly for the purpose of such applications, and Chainlink has been well-positioned to grow exponentially in this space. The brand leads the mission to integrate blockchains with external information sources for greater adoption of this technology.
Investors should feel optimistic about a possible increase in Chainlink’s value. Crypto-rating.com, a reputable machine-learning algorithm for evaluating future prices of cryptocurrencies, had forecasted LINK to be worth around $19.82 in 2021, a price which has already been surpassed.
Conclusion
This article should have provided just the basics of this complex yet fascinating cryptocurrency. To recap, the issue with smart contracts is their limitation to data accessible on the blockchain (on-chain data), which comes from a centralized source.
Chainlink is an assigned decentralized network of oracles to feed accurate real-world data to smart contracts, which then receive LINK tokens for their work. Amid the endless number of existing cryptocurrencies, Chainlink has positioned itself distinctly in the market with a state-of-the-art project that will be hard to duplicate.







