
What is Uniswap? A ‘unicorn’ among the niche decentralized exchange space, Uniswap is an innovative platform for the trading of Ethereum-based or ERC 20 tokens.
Overview
Just as a unicorn in business is rare and sought-after, Uniswap’s logo exemplifies this mythical creature and affirms they are also a unique and precious player in the cryptocurrency market.
Fortunately, the numbers also back this sentiment up as Uniswap is (as of February 9th, 2021) the largest decentralized exchange (DEX) with a daily trading volume of approximately $885 million, occupying about 41% share of the DEX market, according to CoinMarketCap.
Uniswap not only represents an exchange but a utility token (UNI) on its platform, which itself is (at the time of writing) the 15th-largest cryptocurrency globally, boasting a market cap of roughly $5.7 billion and currently valued at $19.16.
This article will cover in broad detail what Uniswap does, how it works, and what makes it the standout performer that it is presently.
Beginnings
Uniswap has many connections to Ethereum, and understandably so. Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum’s co-founder, expressed a vision of decentralized exchanges using an automated market maker system (covered in-depth in a later section).
On the 2nd of October, 2016, Buterin made a post on Ethereum’s subreddit entitled, “Let’s run on-chain decentralized exchanges the way we run prediction markets.”

A former Siemens mechanical engineer named Hayden Adams caught wind of this story from a friend and got inspired. Despite a lack of coding capabilities, Adams obsessively honed those skills and rigorously worked on a proof-of-concept for Uniswap starting from 2017.
Interestingly, one of Adams’ friends initially wanted to call the platform ‘Unipeg,’ a portmanteau of unicorn and Pegasus. Surprisingly, Buterin believed ‘Uniswap’ sounded better.
Adams received a $65,000 grant from the Ethereum Foundation and millions more from notable venture capital firms leading up to the official launch, which occurred on November 2nd, 2018.
How does Uniswap work?
Uniswap is a decentralized exchange deployed on the Ethereum network allowing users to trade or ‘swap’ ERC-20 tokens from their ERC-20 compliant wallets and also list or build new ERC-20 tokens.
You may wonder what ERC-20 is. Technically, ERC-20 ((Ethereum Request for Common, with 20 as the proposal identifier) is an authorized protocol for proposal improvement on Ethereum.
In simpler terms, ERC-20 is essentially Ethereum’s most popular token standard, a language which other tokens on its blockchain follow. A token can represent anything of value, including entire tradeable cryptocurrencies with their own utility, market cap, etc.
Currently, there are at least 200 established digital currencies that are ERC-20 tokens such as Chainlink, Maker, USDCoin, Crypto.com, and so on. All of these coins presently combine to 1,250 paired markets on Uniswap.
Uniswap is also a governance token, affording holders influence regarding decisions over the platform’s core protocol. Another critical point to appreciate about Uniswap is the differences between decentralized exchanges and centralized exchanges (CEX).
CEX vs. DEX
This distinction should help us understand how each exchange primarily operates holistically.
There are many disparities between CEX and DEX, but the main ones are:
- A DEX is non-custodial, while CEX is custodial, meaning that the former doesn’t ‘take custody’ or directly hold one’s funds (while the latter does with in-network wallets). Consequently, CEX wallets are a higher security risk and have been hacked several times, while there is much less chance of hacking on a DEX.
- Ownership on a CEX is attributed to a single entity, while on DEX, it isn’t.
- Furthermore, a DEX charges lower fees than their counterparts, is more transparent, more privacy-centric to personal data & private keys, and offers more control to users.
- A CEX relies mainly on order books for handling customers’ orders, while a DEX generally doesn’t (more covered in the following sub-section).
Liquidity pools
Liquidity pools are an integral part of Uniswap, serving millions of users utilizing countless Ethereum-based applications and tokens. Central exchanges rely on an order book, a mechanism that matches orders of the highest buying (or ‘bid’) prices with the lowest selling (or ‘ask’) prices.
The party facilitating these transactions are ‘market makers.’ Although this model is quite efficient, there may be a liquidity problem, meaning that someone who wants to buy immediately at a certain price may have to wait for an indefinite period until there is a party willing to sell.
Consequently, there may be higher spreads since ‘market makers’ have no incentive to provide liquidity in a thinly-traded market. Furthermore, this model is at the control of the exchange. On the other hand, there is a financial incentive in the form of earning fees on Uniswap for providing this liquidity.
Anyone can lend any of their ERC-20 tokens and assign them to a specific liquidity pool. When someone wants to swap ERC-20 tokens, they will go into this pool and pay a 0.30% fee (the current rate at the time of writing) of the swap volume, all of which goes directly to the liquidity provider rather than the exchange.
This whole mechanism is known as the AMM (automated market maker). The price of each token comes from an algorithm using a ratio of ETH to ERC20 tokens.
Availability and supply
The UNI token is available at many recognized cryptocurrency exchanges. At the start of Uniswap, 1 billion tokens were already pre-minted with a four-year allocation plan in mind.
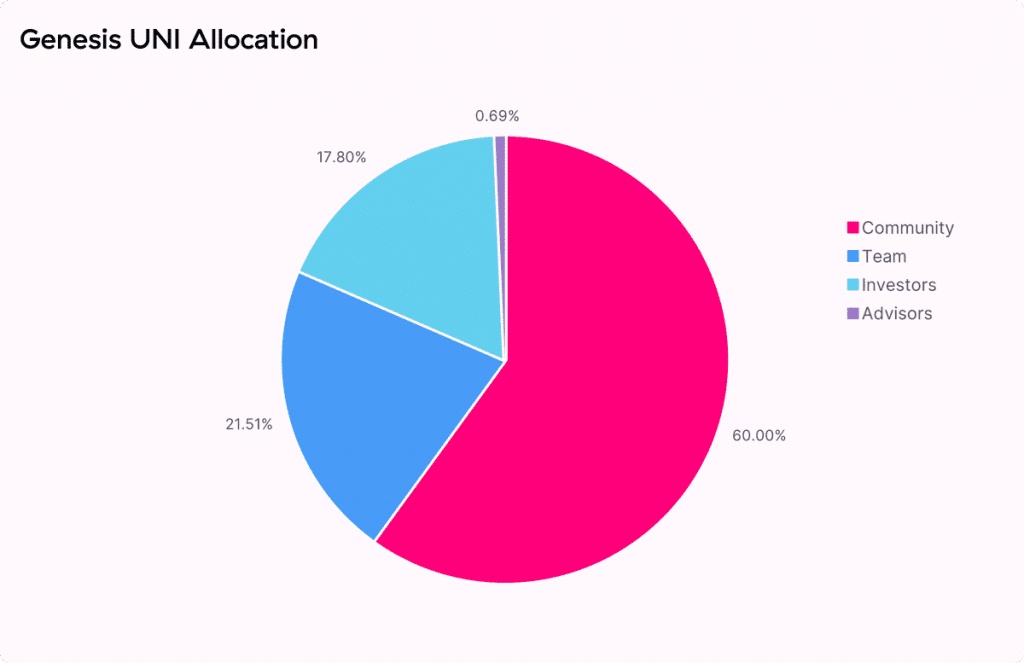
The token distribution stated 60% of these coins would go to users, 21.26% to team members and future employees, 17.8% to investors, and 0.69% to advisors. There is also a 2% perpetual inflation rate planned to start after four years. Currently, there are around 300.9 million UNI in circulation.
What makes Uniswap valuable?
Uniswap turns the centralized exchange model on its head. One of the advantages of a DEX is it doesn’t rely on one single point of failure, drastically lowering the risk of hacking and other security threats, which is one of the core benefits.
Since CEX acts as a middleman, they are obliged to charge a fee for their services. This attribute is absent on Uniswap due to being decentralized. Users have long argued the decentralized nature eliminates the control other established exchanges like Gemini, Coinbase, and Binance currently have.
All the other benefits of DEX against CEX have been outlined in the previous sections, further enhancing Uniswap’s value proposition. Generally, Uniswap is spearheading the ever-growing decentralized finance movement through continual innovation, a space that is one of the most important in cryptocurrencies.
Conclusion
As we’re almost at the end of this article, we should summarise Uniswap is all about solving the liquidity problem without relying on buyers and sellers as it currently is with centralized exchanges.
Uniswap’s roadmap for 2021 is intriguing. One of the planned developments is the upgrade to v3 (currently on v2), improving the AMM experience and governance, among other things.
Uniswap showcases several use cases in the crowded crypto market, making it a truly valuable proposition and a serious contender for eclipsing other established coins very soon.







