
Being the cryptocurrency with the second highest market capitalization after Bitcoin, what is Ethereum? Aside from its native token, Ether used to fuel the ecosystem, Ethereum hopes to disrupt many industries with the power of smart contracts and decentralized applications.
Taking its name from the postulated invisible medium, Ether, which ‘permeates the universe,’ Ethereum is an invention like no other. The Ethereum Foundation, who are the prime developers of Ethereum, describes the network as a ‘global, decentralized for money and new kinds of applications.’
Although most people tend to think of the Ethererum as the currency itself, the technical name for the cryptocurrency is known as Ether (ETH) and functions as the native token on the Ethereum platform.
Cryptocurrency enthusiasts consider the existence of Ethereum to be as significant as Bitcoin, if not more, because of the diverse applications users can derive from the platform. Not only does Ethereum act as a peer-to-peer digital payment service, but it also enables a seamless function of decentralized applications and smart contracts.
Currently and rightfully so, ETH is the second-most traded cryptocurrency with a market capitalization of about $53 billion at the time of writing, according to CoinMarketCap.
Beginnings

Although several people argue about the definitive list of co-founders for Ethereum, the ‘frontman’ most publicly associated with the brand is Russian-Canadian programmer and writer Vitalik Buterin.
The idea for Ethereum was born in late 2013 from a whitepaper where Buterin described the desire for a cryptocurrency that allowed for application development. He failed to gain agreement for turning Bitcoin into this kind of cryptocurrency, prompting his own creation.
Formal development of the project commenced right at the start of 2014 through a Swiss company named, EthSuisse. Before its official launch on the 30th of July 2015, Ethereum successfully raised about $18 million in its ICO (initial coin offering) in August 2014.
How much is Ether worth?
A few years after the launch, Ethereum experienced a meteoric rise identical to Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies. In the crypto boom of 2017, 1 ETH was worth approximately $1382.
As of 19 November 2020, 1 ETH costs roughly $470. Ether is a cryptocurrency available for purchase at numerous currency brokers, cryptocurrency exchanges, and online wallets.
How does Ether work?
As stated previously, Ethereum is the network, and Ether is the currency used to ‘fuel’ it. Ethereum charges developers for the used computing power in their system, which is only payable using Ether.
Aside from being the native currency of Ethereum, ETH can also act as a standalone transaction medium of exchange where transactions are decentralized and peer-to-peer.
Ether’s ledger
Like countless cryptocurrencies, the creation of ETH is courtesy of blockchain technology. Blocks of ETH are stored and grow on an open-source, decentralized, distributed ledger linked through cryptographic hash functions.
Ether’s blockchain uses numerous complex programming languages, namely C++, Go, Python, Rust, and Scala. The mining algorithm for ETH is Ethash, which creates tokens via a proof-of-work consensus mechanism.
Each block takes anywhere between 13 to 20 seconds to form, and the mining reward is 2 ETH per block. The platform can confirm transactions as quickly as 2 minutes on average. As a result of this incredible speed, the circulating supply of ETH is at least 111 million, a figure that grows exponentially daily. There currently is no hard cap on the amount of Ether that will exist.
What are smart contracts?

A smart contract is a self-executing digital contract that can store anything of value like money, content, shares, and property, and execute autonomously. In a real-world manual contract, there typically is a middleman or people who oversee the agreement to ensure validity.
Since a smart contract exists digitally, the conditions coded within it can self-execute without the need for third-party authorization and cannot be changed once in place. This automation results in the entire process being quicker and resistant to fraud and other interference.
What are decentralized applications?
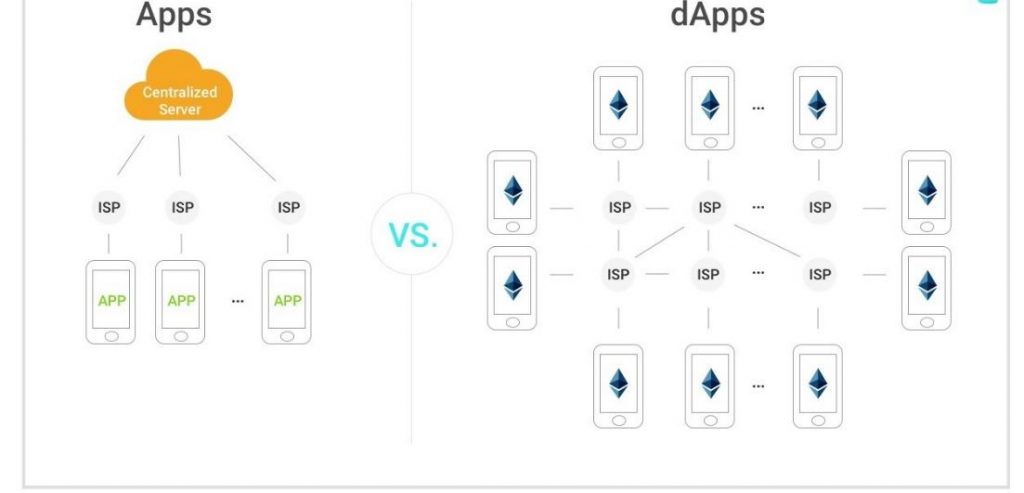
Decentralized applications (commonly referred to as dApps for short) are an extension of smart contracts. A dApp means a computer application that relies on multiple nodes rather than relying on one. Among the core benefits of such applications are:
- Decentralization
- No downtime
- Open-source codes
- Personal data encryption
- Incentives through crypto tokens
And the list above is not exhaustive at all.
Why are smart contracts valuable?
With numerous existing cryptocurrencies already, those interested in such may benefit from knowing what makes a specific coin special and valuable. Ethereum isn’t merely home to another cryptocurrency but it can facilitate other technologies.
As discussed above, these technologies are primarily smart contracts and decentralized applications. Both of these innovations aim to rid centralization.
With smart contracts, the system can create an agreement without a middleman or central authority since it would self-execute after meeting predefined conditions. Selling cars, paying for tickets, and booking hotels are just the tip of the iceberg on how smart contracts can speed up these processes.
Why are dApps valuable?
With decentralized applications, Ethereum will allow anyone with intermediate programming knowledge to build something like a social media app that’s completely decentralized. From a user’s perspective, a dApp prevents censorship from a central authority (compared to an app like Facebook that is centralized), offers token rewards and personal data encryption, among other advantages.
Furthermore, the Ethereum platform is also home to several recognized tokens thanks to the ERC-20 protocol. Currently, the protocol created five of the 20 most traded cryptocurrencies on Ethereum, further illustrating why Ethereum is so valuable.
Future of Ethereum
Many investors are still unsure about Ethereum’s monetary identity in the real world for the future but are bullish on the application aspect. Ethereum 2.0 or Eth2 has been in the pipeline for a few years. A major upgrade to the existing platform would increase the network throughput up to tens of thousands of transactions per second.
The second facet that directly affects miners more about the upgrade is proof-of-stake, where proof-of-work mining will no longer be necessary. Proof-of-stake incentivizes users to stake their coins instead of obtaining rewards from laborious and expensive computer mining.

According to Ethereum themselves, Ethereum 2.0 has the purpose of being more scalable, more secure, and more sustainable. The foundation is set to roll out in December 2020.
Conclusion
This brief overview should help us appreciate the power of cryptocurrencies and what Ethererum will do for everyone. By building a decentralized ecosystem, real-world applications and processes can operate seamlessly, quickly, and securely.
Many analysts predict that Ethereum will be one of several cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin that may be worth several thousands of dollars. Only time will truly tell if this becomes a reality.







